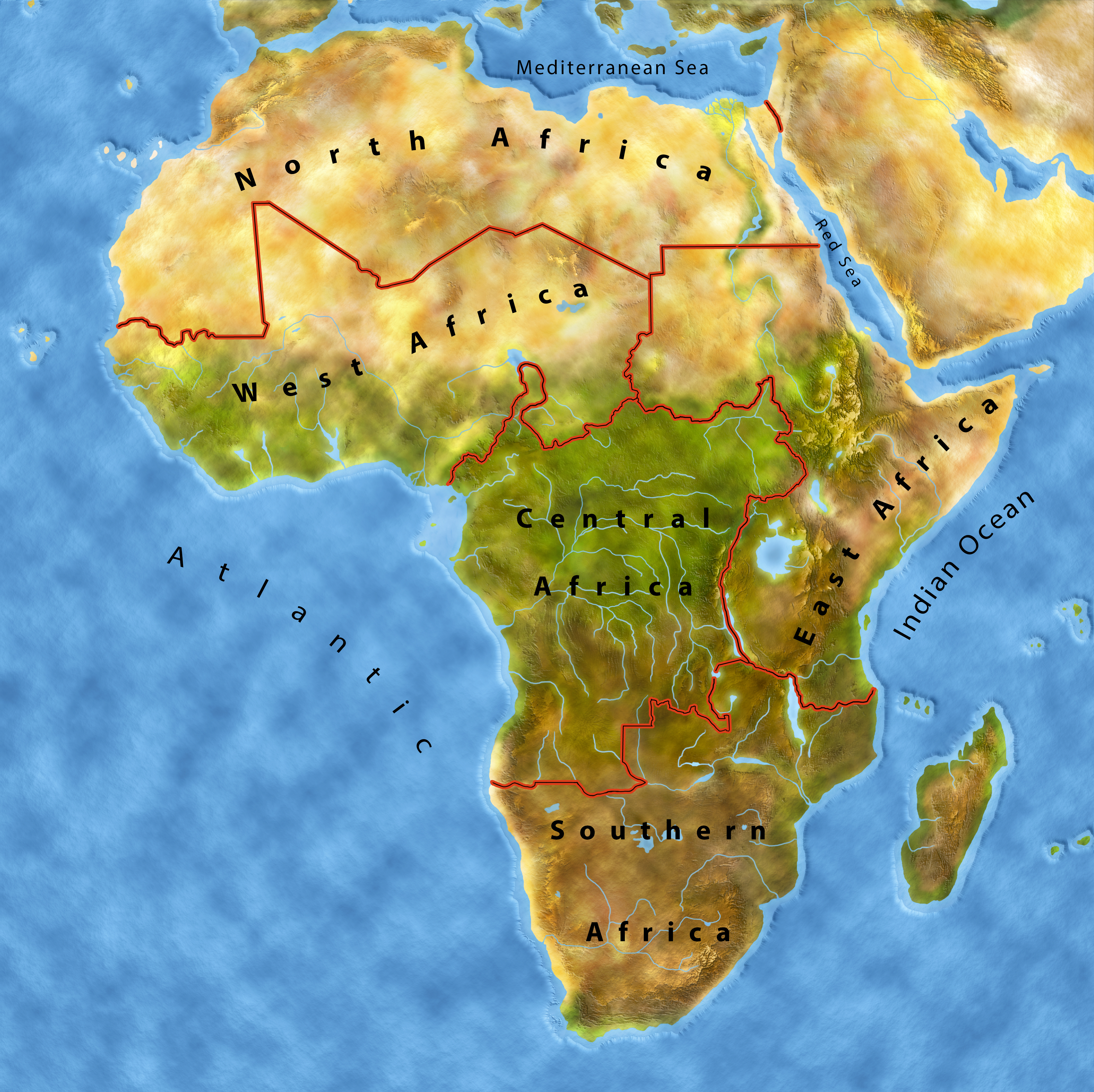
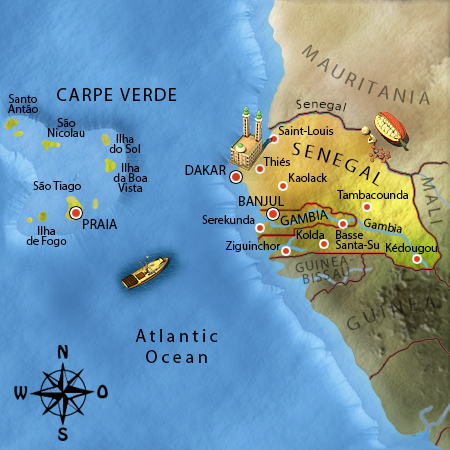
Bonjour, welcome to Senegal, the West African country at the Atlantic!
Senegal is a country in West Africa with a beautiful coastline the the Atlantic. It belongs to the Sahel region along with Mauretania, Mali, Niger and Burkina Faso. These are semi-desert countries with large areas of thorn savannah. It seldom rains and water is rare. Droughts occur very often. The Gambia is a small country surrounded by Senegal.
Landscapes

Lac Retba – The Pink Lake of Senegal
 A special feature of Senegal is the Lac Retba, a salt lake northeast of Dakar. The lake is a deep shade of pink because the water contains pink-glowing microorganisms. Originally the lake was part of a bay. Many millennia ago, the lake became separated off from this bay. As a result of this change, the water in the lake has a very high sea salt concentration, and over time this concentration has increased to ten times that of the sea. People therefore use the lake as a useful source of salt.
A special feature of Senegal is the Lac Retba, a salt lake northeast of Dakar. The lake is a deep shade of pink because the water contains pink-glowing microorganisms. Originally the lake was part of a bay. Many millennia ago, the lake became separated off from this bay. As a result of this change, the water in the lake has a very high sea salt concentration, and over time this concentration has increased to ten times that of the sea. People therefore use the lake as a useful source of salt.
Dakar – Capital city of Senegal
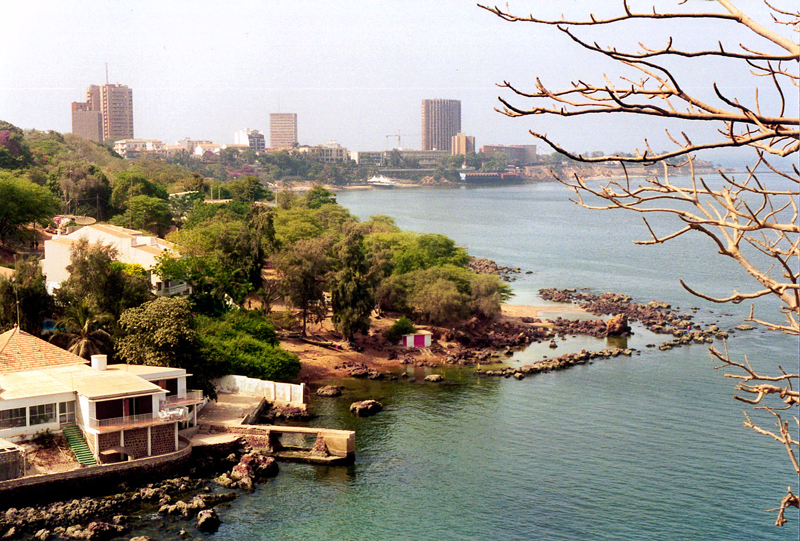 Senegal’s capital, Dakar, is situated on a peninsula on the Atlantic coast and has more than a million inhabitants. Dakar is a modern, lively city where many well-equipped schools, universities and museums can be found. In the town centre there are a number of colourful markets and luxury shops. Dakar has a well-known music scene and many excellent clubs. There is also a harbour and some very lively fish markets.
Senegal’s capital, Dakar, is situated on a peninsula on the Atlantic coast and has more than a million inhabitants. Dakar is a modern, lively city where many well-equipped schools, universities and museums can be found. In the town centre there are a number of colourful markets and luxury shops. Dakar has a well-known music scene and many excellent clubs. There is also a harbour and some very lively fish markets.
The People of Senegal
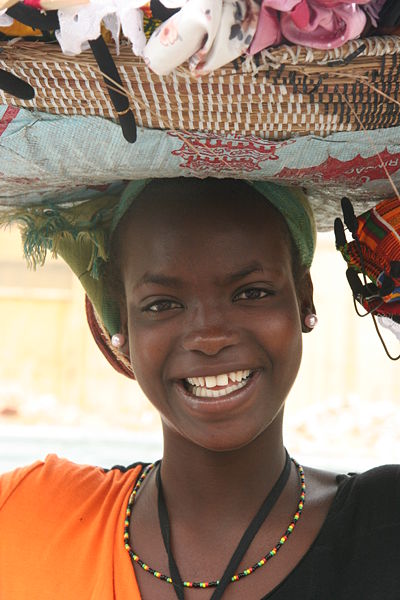

The Wolof people make up the largest ethnic group in Senegal. Their singers and griots are famous throughout Africa. The Serer are farming people based in the west of Senegal. They are well-known for the art of blacksmithing. Many women work in agriculture but just as many work as traders, and have monopoly on the markets. Children start to contribute to the family income at a young age. Cooking together is an enjoyable family event. Millet porridge, yams and fish are important elements of a celebratory meal and food is eaten out of large bowls.
Schools and Education
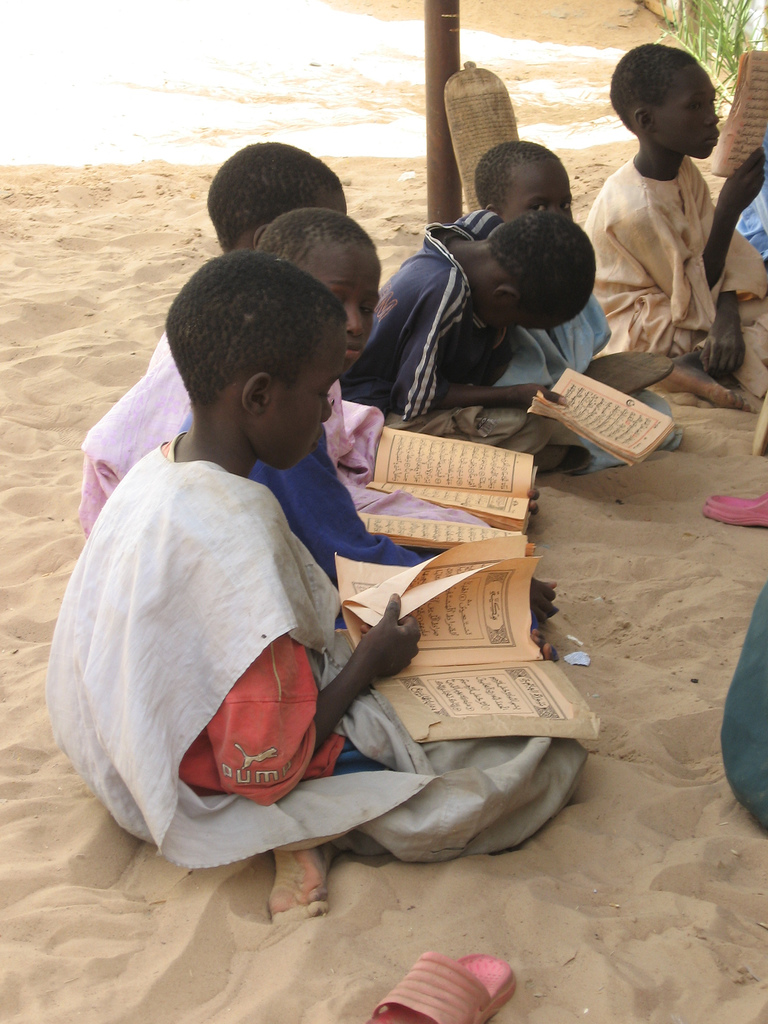

Schools in Senegal are based on the French school system. There are also quite a lot of islamic schools especially for boys. School is compulsory and free up to the age of 16. It is guaranteed that every child shall have access to education. But there are not enough public schools to cope with the number of children that must enroll each year. Therefore quite a lot of children seek education and training by informal means. This is why one third of the children begin their professional live very early, at the age 10 - 14. The Senegales government has begun to build more schools and to improve the educational system so that more children can attend school.
Celebrations, Competitions and Casting shows
 Many followers of the Islam faith reside in Senegal. One of the largest celebrations is the Islamic festival of Eid al-Adha, known in Senegal as “Tabaski”. Here the most prized sheep in the country are searched out, and the best ends up on the feast table. One sheep is then selected as the ultimately prized animal on one of the country’s most popular television shows “Khar Bii”. Similar to western casting shows, proud owners are given the chance to parade their magnificent animals to the public. Every sheep has a name and lives under the same roof as their owner!
Many followers of the Islam faith reside in Senegal. One of the largest celebrations is the Islamic festival of Eid al-Adha, known in Senegal as “Tabaski”. Here the most prized sheep in the country are searched out, and the best ends up on the feast table. One sheep is then selected as the ultimately prized animal on one of the country’s most popular television shows “Khar Bii”. Similar to western casting shows, proud owners are given the chance to parade their magnificent animals to the public. Every sheep has a name and lives under the same roof as their owner!
Did you know? Wrestling is very much part of Senegalese culture? One match can attract 80,000 spectators and millions of TV viewers.
Economy and Natural Resources
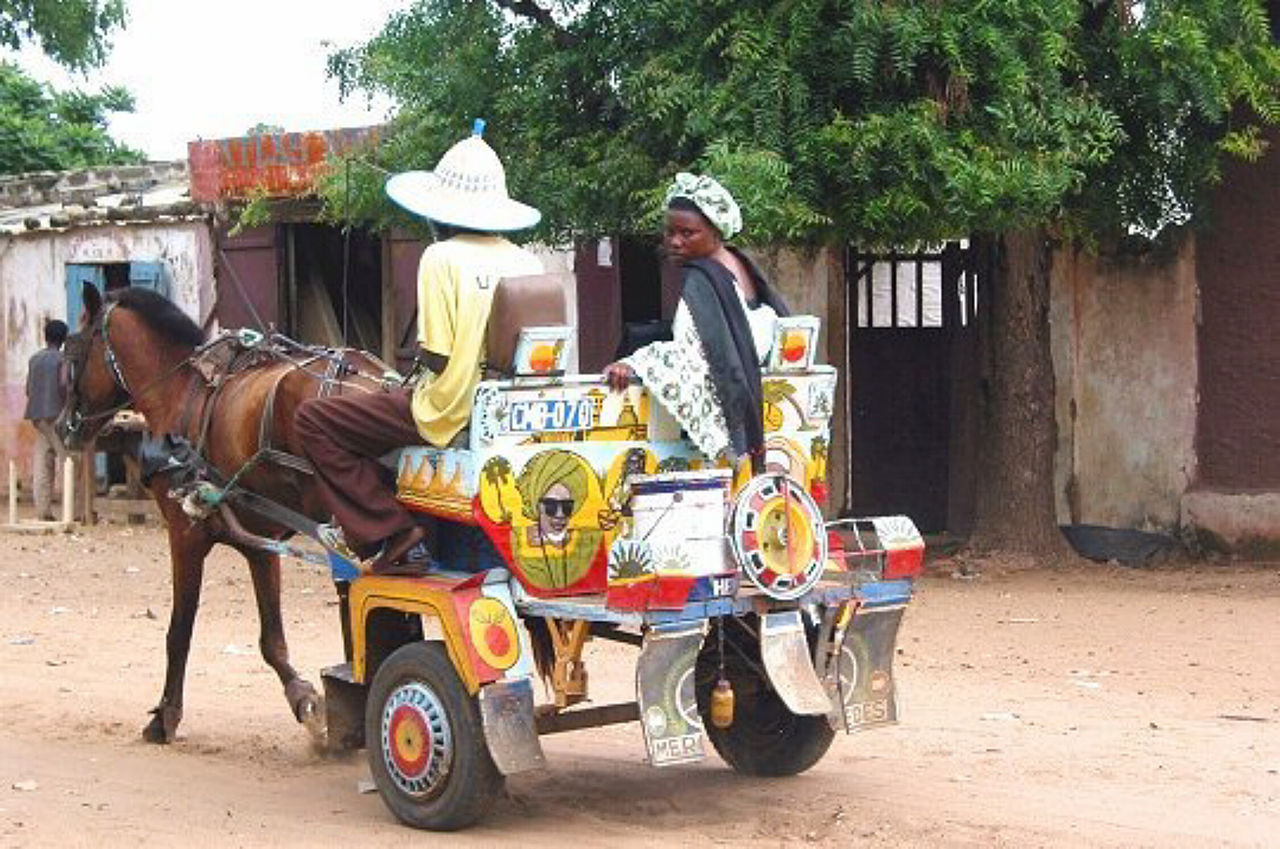 Senegal has only a few natural resources. Most of the people live of fishing and agriculture. One of the most important food products is peanut oil, which was Senegal's top agricultural-based export. Many of the country’s factories are involved with the processing and refining of agricultural products. Textile, shoes, trucks and cement are industrial produced products, that are also exported. Since several years, Senegal’s tourism sector is rising.
Senegal has only a few natural resources. Most of the people live of fishing and agriculture. One of the most important food products is peanut oil, which was Senegal's top agricultural-based export. Many of the country’s factories are involved with the processing and refining of agricultural products. Textile, shoes, trucks and cement are industrial produced products, that are also exported. Since several years, Senegal’s tourism sector is rising.
History of Senegal
 From the 9th Century, Senegal was taken over by the Islam faith. The largest African kingdoms of the Middle Ages developed in the Sahel region. Takrur was a large empire in Senegal. It was established by the Serer people on the Senegal River and developed into an important centre of trade. Takrur’s supremacy was given over to the Mali Empire in the 14th Century. Learn more about the medieval Mali Empire.
From the 9th Century, Senegal was taken over by the Islam faith. The largest African kingdoms of the Middle Ages developed in the Sahel region. Takrur was a large empire in Senegal. It was established by the Serer people on the Senegal River and developed into an important centre of trade. Takrur’s supremacy was given over to the Mali Empire in the 14th Century. Learn more about the medieval Mali Empire.
The Colonisation of Senegal

In 1444 the first Portuguese ship reached the coast of Senegal. In the 17th Century Senegal was colonised by the French, Dutch and British. By 1891 Senegal was completely under French control, explaining why French is the official language in the country today. Many people in Senegal also speak an African language alongside French, for example, Wolof. On 20th August 1960, Senegal was made independent and is considered today to be one of the few democratic states on the entire African continent.
![]() More about the Kingdom of Mali
More about the Kingdom of Mali
Senegal Today
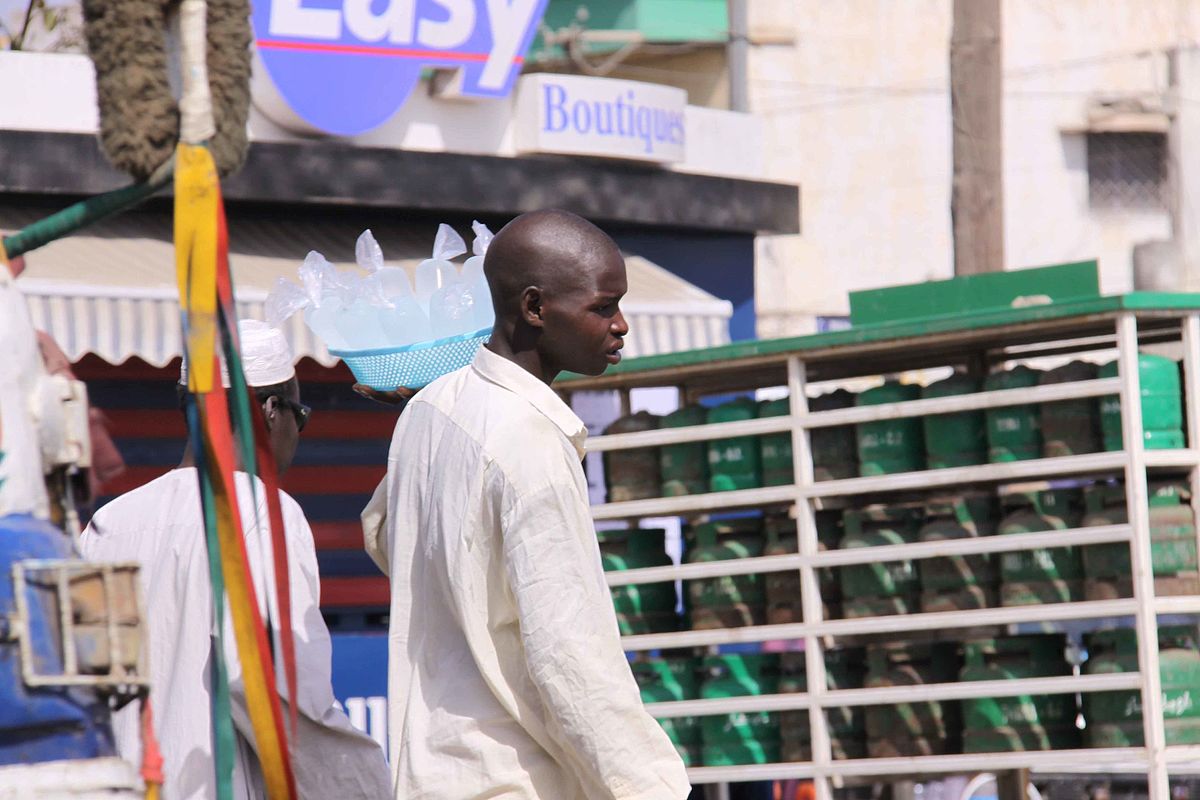 Senegal became fully independent in 1964. Léopold Sédar Senghor was the first president. Today Senegal is considered one of Africa's model democracies. The western African nation has a tradition of stable governments and civilian rule. Senegal is one of the most visited countries in western Africa. The country is very colourful, the people take a pride in their long and patterned traditional clothes. But there is also the modern Senegal with its industries, universities and music clubs.
Senegal became fully independent in 1964. Léopold Sédar Senghor was the first president. Today Senegal is considered one of Africa's model democracies. The western African nation has a tradition of stable governments and civilian rule. Senegal is one of the most visited countries in western Africa. The country is very colourful, the people take a pride in their long and patterned traditional clothes. But there is also the modern Senegal with its industries, universities and music clubs.