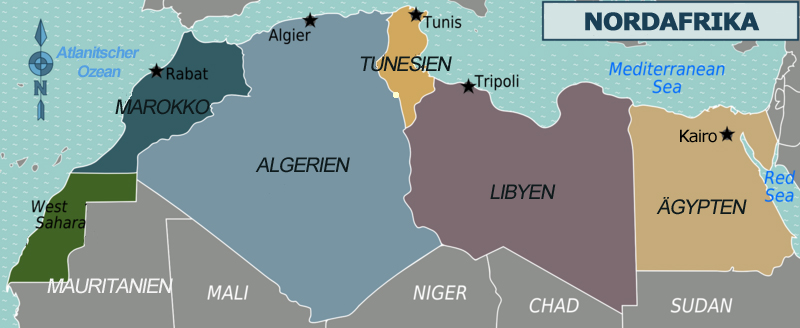
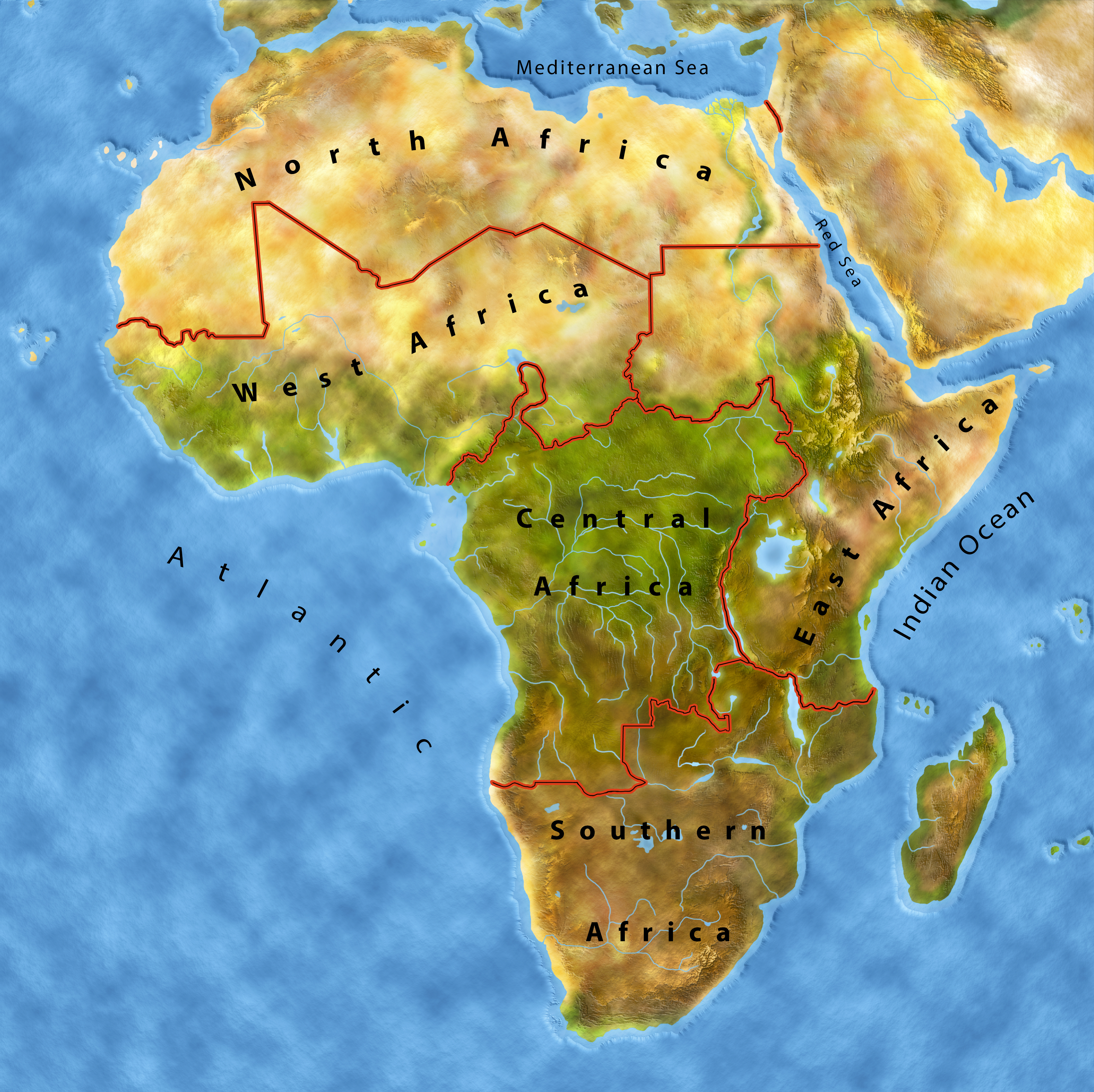
The Sahara Desert covers almost all of North Africa. It is almost the biggest desert in the world! Only the Antarctica is bigger.
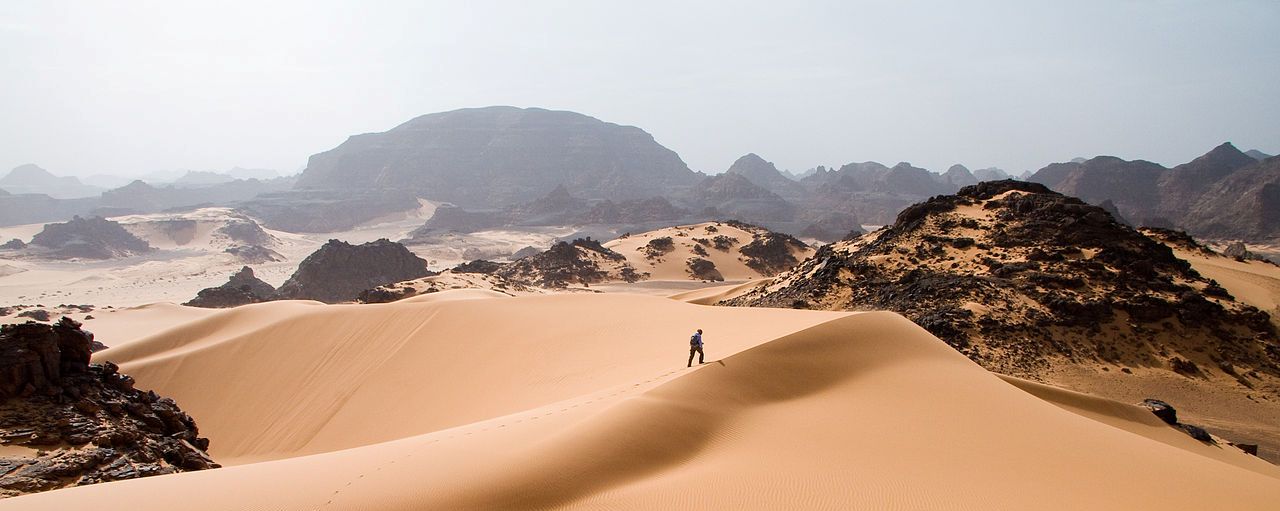

Imagine nine million square kilometres with barely any water, just dunes, mountains and sand. But it wasn’t always like this. In our planet’s early days, the desert consisted of lakes and fertile land. How do we know that? Through hundreds of wale skeletons that were found in the desert sand. The eldest peoples depicted the Sahara Desert as a fertile land with elephants, giraffes or antelopes, which today only live in the savannah south of the Sahara. However, through thousands of years the climate changed and the fertile land turned into desert. Animals and humans moved to the few lakes, oases and rivers.
The Desert is hot like an Oven
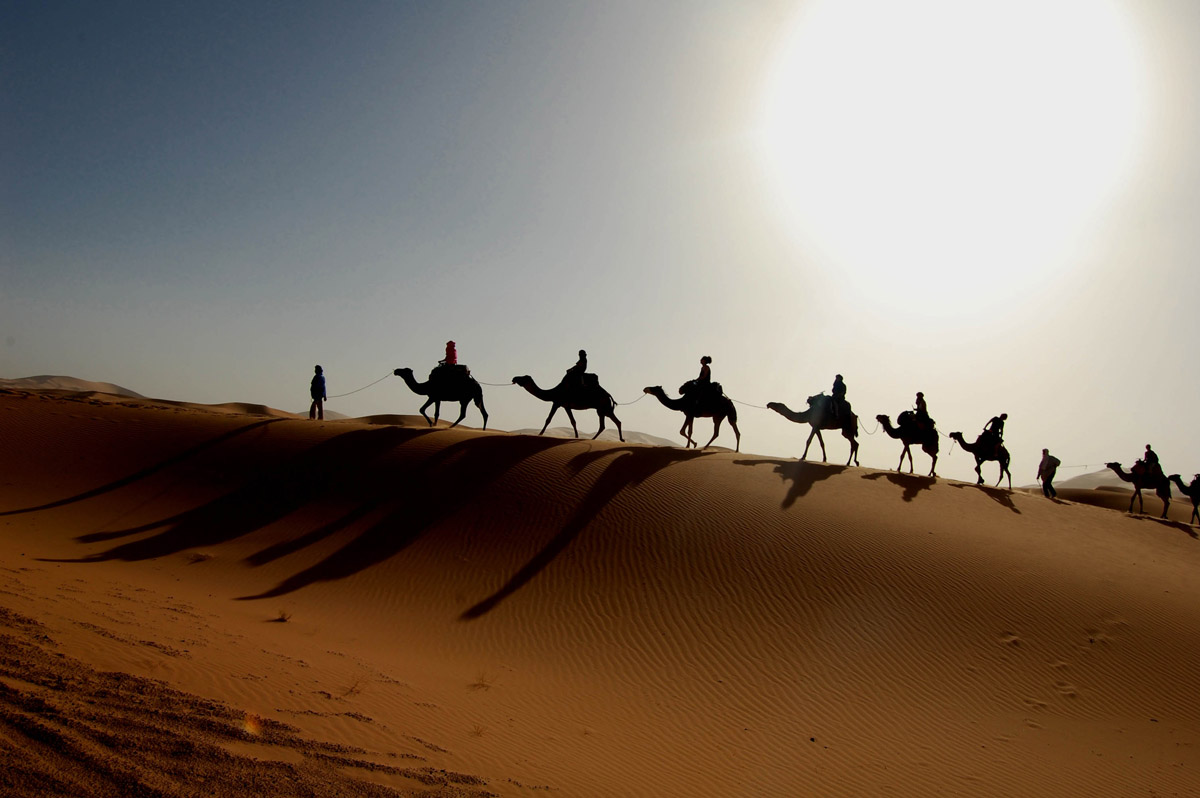

During the day, the Sahara Desert is like an oven, temperatures rise up to 50 degrees and more. At night, it is like a fridge, since temperature drop under zero degrees. The Libyan Desert is the sunniest, the driest and the most nearly rainless place on the planet. Only few peoples can cope with the drought of the desert. The Sahara includes sand dunes, mountain ranges, desert shrub, wadis and oases.
Animals of the Sahara
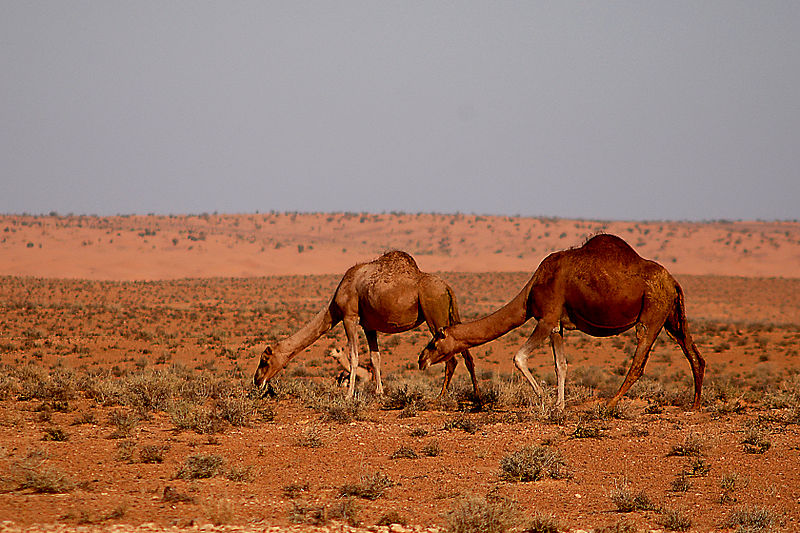

To survive in a desert is very hard. There is barely any water, no shade, no protection from predators. That is why only the most frugal animals can survive here, such as camels and dromedaries, desert foxes, scorpions and white scavenger vultures.
![]() More about the animals of the Sahara Desert
More about the animals of the Sahara Desert
Snow in Africa
The Atlas Mountains are a series of mountain peaks that run along the northwest of Africa. The mountain range is extending through Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia. The Atlas Mountains seperate the coast from the desert. It is particularly difficult to cross due to its extremely high peaks. The Jbel Toubkal in southwestern Morocco is reaching 4,167 meters at its high point. In the winter it is covered with snow that lasts well into late spring. Indeed, you can go skiing in the High Atlas Mountains.
A river through the Desert

The Nile River is the longest river on Earth. Its source is in the highlands of Ethiopia and flows through the Sahara Desert. Once a year, the Nile river floods the fields and creates fertile farmland. Without it, the Egyptian Pharaoh Empire would have not existed. The best way to explore the Nile River is with a felucca, a wooden boat with a sail.
Oases in the Sahara Desert
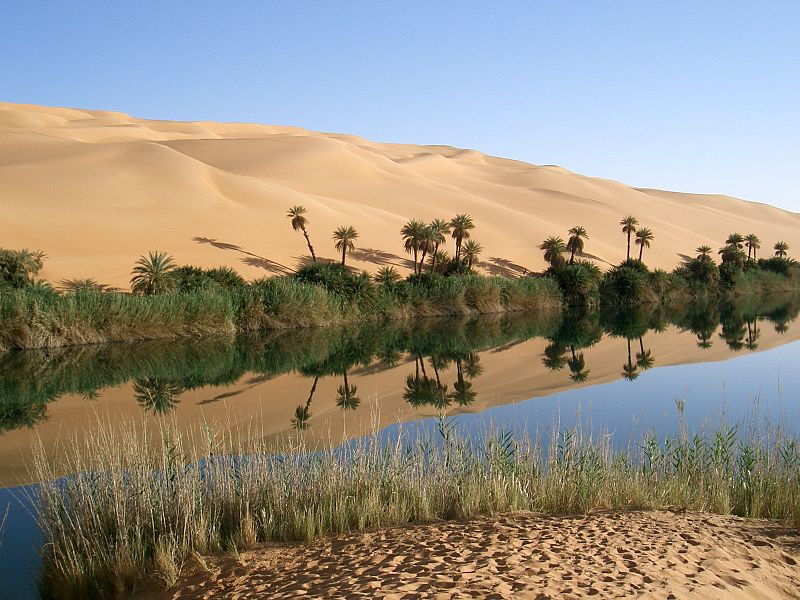

The road networks in the Sahara Desert have developed along oases. Oases are small natural lakes or deep wells, at which nomads, cattle breeders and salt caravans fill up their water supplies for their long journey through the river and where they exchange goods. Some oases have so much water available that date palm groves and vegetables can be planted.
The Nomads of the Desert
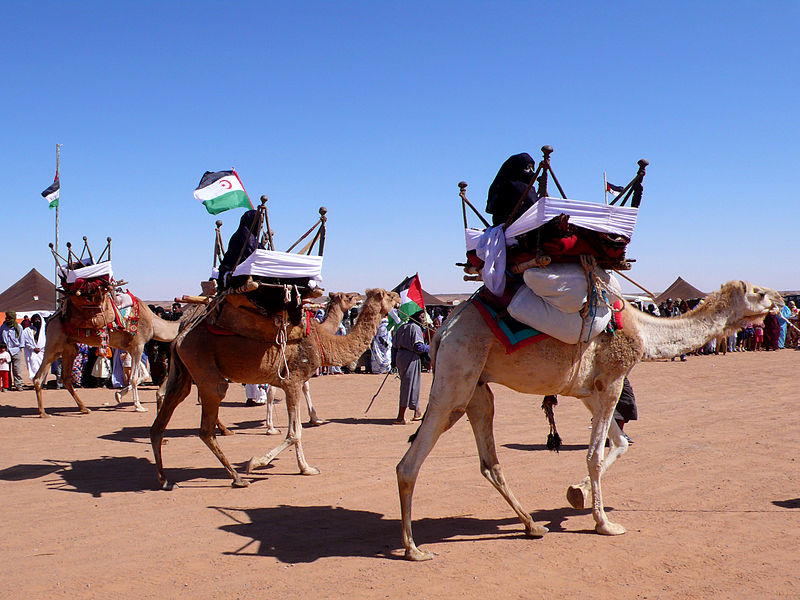

The Sahara Desert is inhabited by about two million people. That is a very low number in comparison to the USA, where about 300 million people live on a surface area of the same size. Only few nomad tribes can cope with the extreme drought of the Sahara Desert. One of them are the Tuareg people, also called the “blue” people of the desert. They travel through the Sahara with their salt caravans. They have learnt to protect themselves from the sun, the wind and the sand. They don’t have any maps, but they find their way with help of the sun and the stars. They know every rock and every source of water.
Palm trees, the desert trees
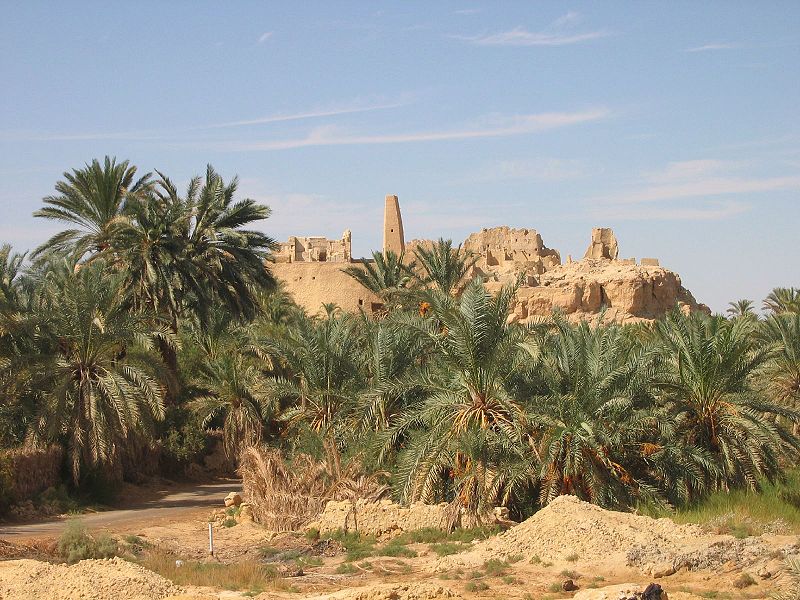

No trees grow in the desert, except for in oases. The ancient water reservoirs, which are embedded deeply into the earth, let palm trees and other plants thrive at these places. Why palm trees? This tree species is able to let its roots grow up to 50 metres deep. Here, they come upon the underground water reservoirs of the Earth, from which they feed. There are no singular palm trees in the Sahara Desert, because they grow in groups in the oases.